There are different surgical procedures for the Hallux rigidus. We talk about conservative surgical treatment when the intervention allows to simply correct joint deformation or non-conservative treatment when the intervention requires blocking the joint (arthrodesis) or replacing it with an implant (prosthesis).
The technique can be percutaneous, i.e : the surgical procedure is performed by one or more mini incisions of a few millimeters and under radiographic or arthroscopic control.
Conservative surgical treatment
- The first step is to flatten the upper bone with a motorized cutter.
- Secondly, an osteotomy can be performed to make the joint more anatomically oriented and to limit compression stresses.
- Finally, it may be necessary to raise the toe by acting on the ligaments.
Arthrodesis
For this procedure the first surgical time is identical to that of the conservative treatment. Then, the surgeon blocks the joint by fixing the metatarsals and the first phalanx of the toe with two screws..

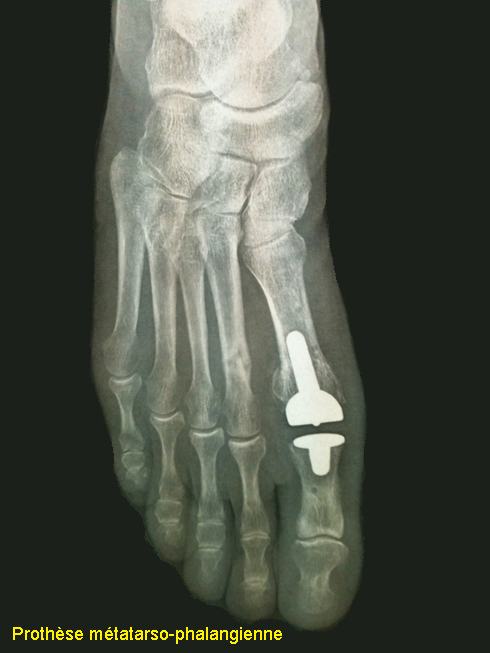
The joint prosthesis
This procedure involves replacing the joint with a prosthesis, which keeps the mobility.
- Anesthesia : loco regional
- Technique : mini invasive
- Hospitalization : outpatient care
- Immobilization : immediate walking with forefoot shoe
- Rehabilitation : from the 3rd week after surgery


